
Many children and teens are developing video game-related disorders. Gaming disorder, which is also known as internet gaming disorder or video game addiction, is associated with a range of behavioral changes. These patterns of behavior often have negative short- and long-term effects on a child’s development, physical health, mental health, and social health.
About Video Game Disorders:
What Is A Video Game Disorder?
What Are the Symptoms of Gaming Disorders?
Who is at Risk of Developing a Gaming Disorder?
Children and Video Game Obsession
How Can I Tell If My Child Is Addicted to Video Games?
What Games Cause Gaming Disorder?
Can People File Lawsuits For Gaming Disorders?
Contact King Law for More Information on Filing a Video Game Lawsuit
What Is A Video Game Disorder?
A video game disorder is a condition in which an individual shows reduced control over habits related to video games, resulting in damaging effects in other areas of life, including:
- Work
- School
- Relationships
- Physical health
- Relationships
- Self-care
- Mood
These effects are similar to those observed in individuals suffering from chemical (e.g., drug or alcohol) addiction.
Prevalence rates of video game addiction vary widely. Within the medical community, diagnostic criteria vary depending on the guidelines used. One literature review found a general prevalence rate between 0.5% and 9.9%, with higher rates observed in Asian countries and among males. Individuals with higher traits of neuroticism (a tendency to experience negative emotions), impulsivity, and aggression were more likely to have a video game addiction. Higher scores in video game addiction were correlated with symptoms of inattention, anxiety, and depression.
While individuals of any age can develop a video game disorder, children may be especially vulnerable to the condition. A study conducted in Saudi Arabia of 393 adolescents aged 12 to 16 found that 62.1% of the 393 surveyed had symptoms of video game addiction. This points to a high prevalence of video game disorders among tweens and teens.
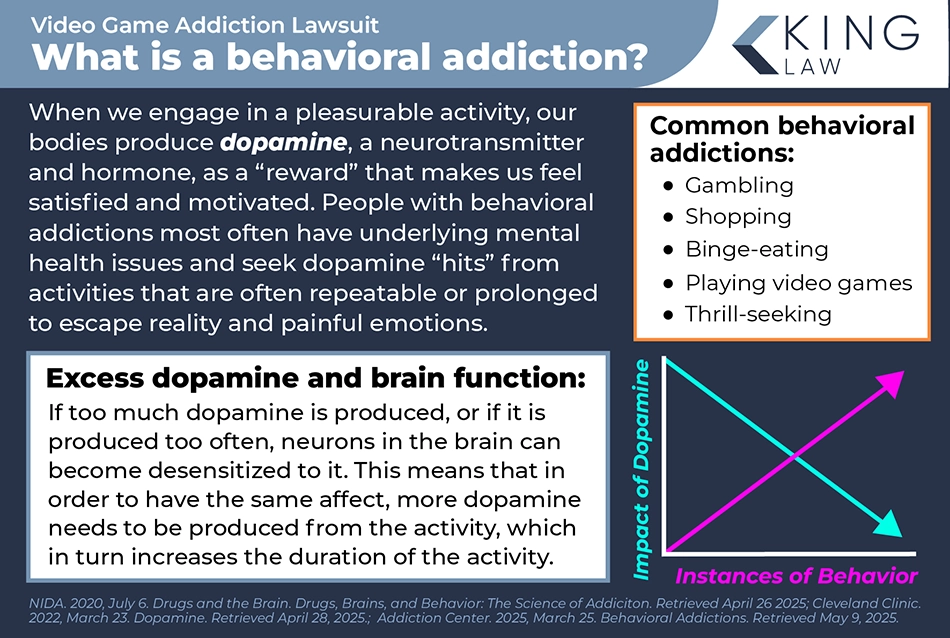
Recognized Gaming Disorders
Research into gaming disorders is ongoing, and there is some disagreement among researchers over whether to classify gaming disorder as an addiction or a form of mental illness. However, gaming-related disorders are currently recognized by medical entities.
The World Health Organization (WHO), for example, outlines a condition it calls “gaming disorder.” Meanwhile, the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5-TR) describes a condition it calls internet gaming disorder (IGD) and calls for further research into how the condition should be classified and treated.
Gaming Disorder
The WHO defines gaming disorder as “a pattern of gaming behavior (“digital-gaming” or “video-gaming”) characterized by:
- Impaired control over gaming
- Increasing priority given to gaming over other activities
- Choosing video games over important activities
- Continuation or escalation of gaming despite experiencing negative consequences
If someone is suffering from gaming disorder, they display patterns of behavior that result in significant impairment to their social, personal, occupational, or educational functioning. The pattern should also typically be observable for at least 12 months.
The WHO notes that only a small proportion of video gamers, including children, would qualify as having a gaming disorder under its current diagnostic criteria. However, it is urging scientific professionals to conduct additional research about gaming disorders.
Internet Gaming Disorder
In comparison, more children could be considered to have an internet gaming disorder under the DSM-5-TR’s diagnostic criteria. In fact, a study of over 7,000 Mexican university students that tested both sets of diagnostic criteria found prevalence rates of internet gaming disorder (DSM) to be two times higher than gaming disorder (WHO).
Qualifying for internet gaming disorder under the DSM-V requires experiencing five or more symptoms of the disorder within a year.
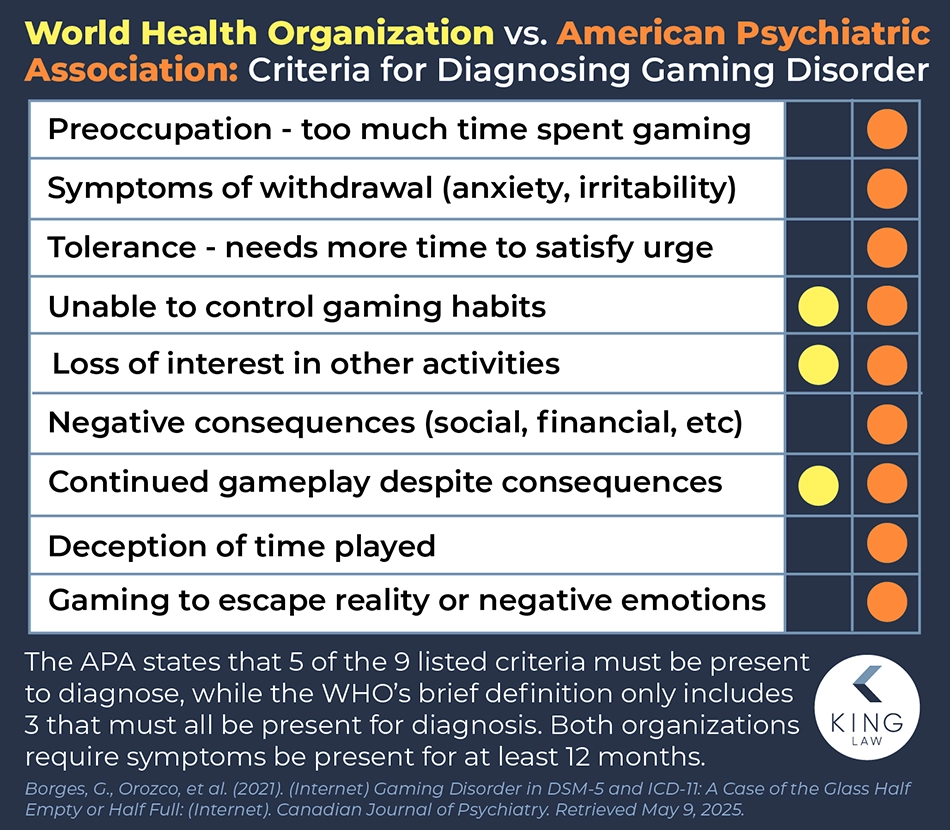
What Are the Symptoms of Gaming Disorders?
Regardless of the diagnostic criteria used, gaming disorders present with identifiable symptoms. For example, the DSM-V-TR’s list of symptoms includes:
- Preoccupation with gaming
- Withdrawal symptoms
- Inability to reduce play time
- Deceptive behavior, such as lying about the amount of time spent gaming
- Losing interest in other activities
The Mayo Clinic notes that video game addiction can take the form of chronic hyperarousal due to the brain being overstimulated by intense simulated scenarios. Hyperarousal can present as irritability, depression, isolation, and reduced empathy. Physical symptoms related to too much screen time may include obesity, insomnia, eye strain, and neck and back problems.
What Causes Video Game Addiction?
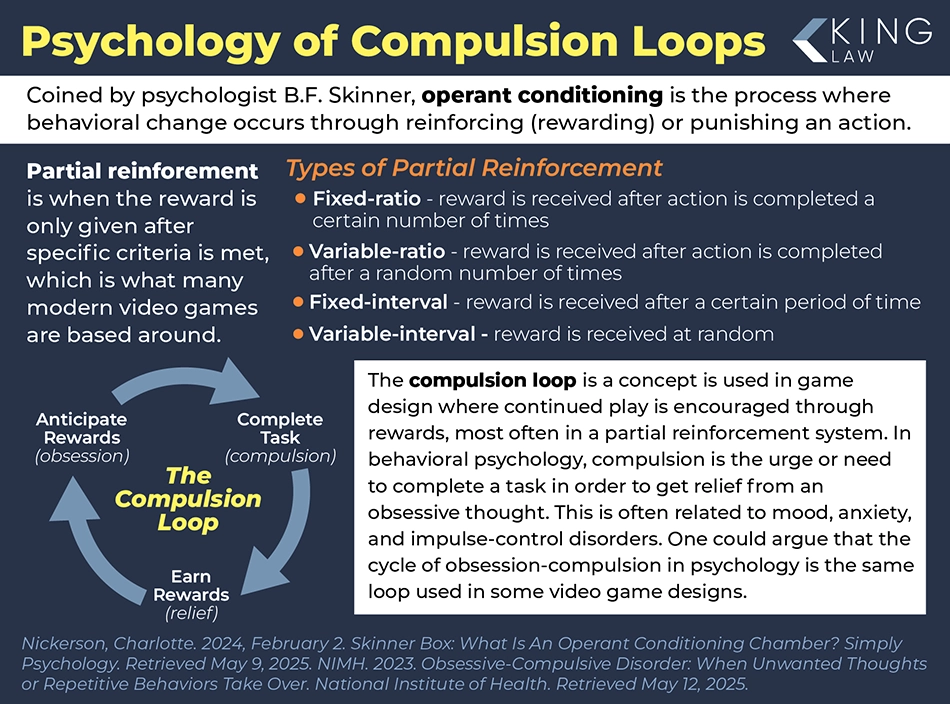
Video game designers frequently employ the concept of compulsion loops in game design. A compulsion loop is a set of activities that are reinforced using an external reward system. For example, a player may be incentivized to perform a task by being rewarded with in-game experience points, currency, cinematics, or platform-based achievements/trophies. After the reward is received, another task is given with the promise of another reward. Some games have more aggressive compulsion loops than others, particularly those that monetize frequent player interactions through daily rewards and microtransactions.
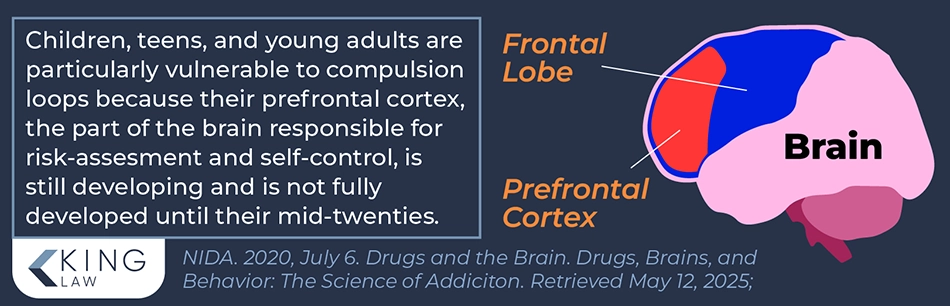
Children and teens tend to be more vulnerable to addiction due to their developing prefrontal cortices (brains), which are associated with self-control and risk assessment. Adolescents, in particular, are likely to experience more intense reward sensations from both substances and activities like video games.
Who is at Risk of Developing a Gaming Disorder?
Not all children are equally at risk of developing a gaming disorder. A Spanish study found an association between internet gaming disorders and the following traits:
- Impulsivity
- Aggressiveness
- Hostility
- Sensation seeking
- Social withdrawal
Additionally, the study found characteristics in common with depression, anxiety, and attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Traits like strong self-esteem, self-identity, and interpersonal relationships had a negative association with internet gaming disorder, meaning they were less likely to be present in combination with it.
Another study found links to broader attention and cognitive control issues, including ADHD, as well as social vulnerability. The study defined social vulnerability as the degree of difficulty one experiences in forming and maintaining friendships.
Gaming and Mental Health
A study on video game-related pathology notes that video game playing is not always associated with negative social, physical, or psychological outcomes. In fact, games can be very effective at teaching skills through their systems of trial, replay, and reward. These same traits, however, can lead to video game addiction in vulnerable players.
Video game addiction is associated with a variety of mental health issues, including:
- Decreased life satisfaction
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Reduced academic achievement
- Increased aggression and impulsivity
- Executive functioning issues (ADHD)
Lawsuits against specific video game companies, including those taken on by King Law, allege that certain games are knowingly designed to encourage addictive patterns of behavior in young people.
Children and Video Game Obsession
Children tend to be more vulnerable to addiction, and video game obsession is no exception. Children and their developing brains have a harder time with impulse control, a trait associated with video game addiction. Video games can provide a quick and relatively easy hit of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which creates a feeling of reward. This can train the child to expect immediate rewards for trivial effort in other areas of life. Excessive dopamine triggering may also reduce impulse control.
Video games present a stimulating palette of colors, motions, scenarios, and interactivity that simulate intense scenarios. At the biochemical level, these stimuli can create an arousing fight-or-flight response and sense of anticipation. Some developers intentionally optimize their to hook players through more frequent and compulsive dopamine rewards. Video game makers may also try to entice young people through social features that create peer pressure by allowing players to show off their characters, items, and creations.
One particularly controversial tactic is the use of loot boxes, which is a common feature in otherwise free-to-play “gacha” games. Loot boxes are randomized bundles of in-game goods sold as microtransactions or given as a reward to the player for in-game achievements. Players are incentivized to spend money or time in the hope that they will randomly pull a powerful item or character from a particular loot box. Some countries have banned or restricted the use of loot boxes in video games, classifying them as a form of gambling. Countries that have restricted loot boxes include:
- Belgium
- The Netherlands
- Germany
- Australia
- China
- South Korea
- Taiwan
What Should Parents Do If Their Children Are Obsessed With Video Games?
Parents who believe their child has problematic gaming habits should consider setting firm conditions on when video games can be played and for how long. Restricting the number of hours a child can play per week, offering game time as a reward for good behavior, and steering the child away from particularly addictive games can help a child develop a healthier relationship to gaming. Most modern game systems provide parental controls to help enforce limits on a child’s video gaming.
How Can I Tell If My Child Is Addicted to Video Games?
If you suspect your child may be addicted to video games, you should both monitor the amount of play time your child engages in and be alert for any withdrawal symptoms. These can include:
- Sadness or irritability when access to games is taken away
- Increasing tolerance, i.e., the need to play longer to get the same levels of satisfaction
- Lying about the amount of time spent playing
If your child has difficulty restricting their gaming habits on their own, communicating your concerns and helping them understand their gaming patterns can help them establish a healthier relationship with their hobby.

How Do I Know If My Child Has Crossed the Line From Gaming Into A Gaming Disorder?
Most children and teens who play video games do not develop a gaming disorder. For video gaming to be considered a disorder, it must lead to serious negative effects on the child’s mood, functioning, or health over a prolonged period, typically a year.
A psychologist or psychiatrist can help diagnose an internet gaming disorder using DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. This will involve asking questions about the child’s health and gaming behaviors.
How Many Hours Does Video Game Addiction Typically Involve?
Video game addiction generally involves substantial time commitments to gaming. For example, an addicted gamer may spend over three hours a day gaming for five weeks or more. However, time spent gaming generally is not always a strong measure of video game addiction. Most diagnostic criteria focus on symptoms of stress and withdrawal, as well as disruptions to social, academic, and work life.
What Games Cause Gaming Disorder?
Not all video games are equally likely to lead to a gaming disorder. Certain games employ specific features and design strategies that encourage and reward compulsive play. Examples of features that can trigger addictive behavior include:
- Compulsion loops: Repeatedly encouraged and reinforced patterns of anticipation, activity, and reward. These are common in video games in some form, though the intensity and frequency of these loops vary.
- Endless gameplay: Games with no end goal, levels/chapters, or clearly delineated stopping points can make it difficult for players to self-regulate play time.
- Random rewards: By offering unpredictable rewards for achieving goals, games can encourage gambling-like behavior in players, who will be encouraged to compulsively play in hopes of scoring the game’s version of a jackpot.
- Microtransactions: A monetization model for games that encourages repeated, small-value purchases to unlock in-game perks or customizations. It’s especially common in “free-to-play” (sometimes called “gacha”) games, which offer a taste of the game’s compulsion loops before locking progress behind paid gateways. This model can lead to players compulsively spending far more on a “free” game than they would on a full-priced game.
- Social features: By encouraging interaction with other players, games may compel players to play through peer pressure. This can include allowing players to see status-signaling items or achievements possessed by other users that the player will then be encouraged to earn through play or purchase.
Games that combine two or more of the features above may have an even higher risk of addiction.
King Law is pursuing action against the makers of a number of games that possess these qualities. These developers are being accused of knowingly adding addictive features to their games and failing to disclose the risks to which they may subject vulnerable players:
- Call of Duty (Activision)
- Overwatch (Activision)
- World of Warcraft (Activision)
- Apex Legends (Electronic Arts)
- Counter-Strike (Valve)
- Fortnite (Epic Games)
- Grand Theft Auto (Rockstar Games)
- League of Legends (Riot Games)
- Minecraft (Mojang Studios)
- Rainbow Six Siege (Ubisoft)
- Roblox (Roblox Corporation)
- Rocket League (Psyonix)
- Valorant (Riot Games)
The PlayStation and Xbox platforms have also been implicated in some of these legal actions.
Can People File Lawsuits For Gaming Disorders?
Individuals who believe they suffer from video game disorders may be able to file a lawsuit if they meet certain criteria. To establish a strong case, individuals will need to show:
- That they have suffered damages related to a medically diagnosed disorder linked to video games.
- Proof that they have played specific games on specific consoles for more than 3 hours a day for a period of at least 5 weeks.
- They have been playing the implicated games before the age of 24 and were diagnosed with a qualifying disorder before the age of 25.
Qualified individuals may be able to recoup damages for medical bills, lost wages, expenses related to gaming (like microtransactions), and non-economic damages like emotional distress.
Can Parents File a Lawsuit if Their Child Has a Video Game Disorder?
Parents can file on behalf of their minor-aged children if their child meets the requirements for a video game disorder lawsuit. The child may also be entitled to additional compensation due to damages to their development caused by a video game disorder.
Contact King Law for More Information on Filing a Video Game Lawsuit
King Law has decades of collective experience holding large corporations, like video game developers and publishers, liable for misconduct and negligence. Contact our office for a free consultation to see if you’re eligible to take legal action against video game companies.

